Ceribell is the FIRST critical care monitoring and neurodiagnostic device to achieve both



The first critical care monitoring device and neurodiagnostic to achieve both FDA Breakthrough Designation and a New Technology Add-on Payment (NTAP) code from CMS.



Clarity
is an artificial intelligence-based software algorithm that analyzes EEG
waveforms to diagnose electrographic status epilepticus. The Clarity
algorithm offers continuous monitoring of
patients for potential seizure activity, providing both bedside and remote
clinicians with vital real-time data. The advanced software enables swift
identification and treatment of seizures, as well as guides precise medication
management.
Efficient
and Actionable EEG Reads



With
Clarity, the Ceribell solution allows hospitals to efficiently expand their
brain monitoring capabilities to acute care departments, at a fraction of the
cost of conventional EEG.
For questions, click on the button below and a member of our team will contact you.
Contact Us
The FDA Breakthrough Devices Program is intended to provide
patients and health care providers with timely access to medical devices by
speeding up development, assessment, and review for premarket approval, 510(k)
clearance, and De Novo marketing authorization.
Breakthrough
Devices must meet the FDA's rigorous standards for device safety and
effectiveness, including providing for more effective treatment or diagnosis of
life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating diseases or conditions and
offering significant advantages over existing approved or cleared alternatives.
Clarity is
now the only FDA-indicated device for the diagnosis of ESE in adult patients
over the age of 18. Moreover, this is the first time in a decade that the FDA
granted a diagnosis designation to an acute care device.

The New Technology Add-on Payment (NTAP) is a Medicare
reimbursement program that financially assists healthcare organizations when
they adopt new technology and is part of the CMS Inpatient Prospective Payment
System (IPPS). CMS grants New Technology Add On Payments (NTAPs) to
breakthrough devices to stimulate the use of new technology. Only
traditional Medicare beneficiaries are eligible for NTAP reimbursement.
Receiving NTAP is further validation of Clarity’s
clinical impact, as NTAP eligibility requires:
1) Newness:
A technology is considered new until the claims data becomes available
(typically
up to 3 years after FDA approval) and so long as it is not
“substantially similar” to existing technology
2) Cost:
The
technology must be inadequately paid
under the existing MS-DRG system
3) Substantial Clinical Improvement:
Use of the technology must
significantly
improve clinical outcomes
for a specified patient population, compared to
currently available treatments
NTAP approval for additional reimbursement for eligible Medicare patients became effective on October 1, 2023. Additional reimbursement (NTAP) per eligible patient is exclusive to Clarity.

Clarity is
an updated algorithm package designed to enable more efficient patient
diagnosis and management, making it possible for even the busiest of hospitals
to provide comprehensive care for suspected seizure patients.
There are
three key new features with Clarity:



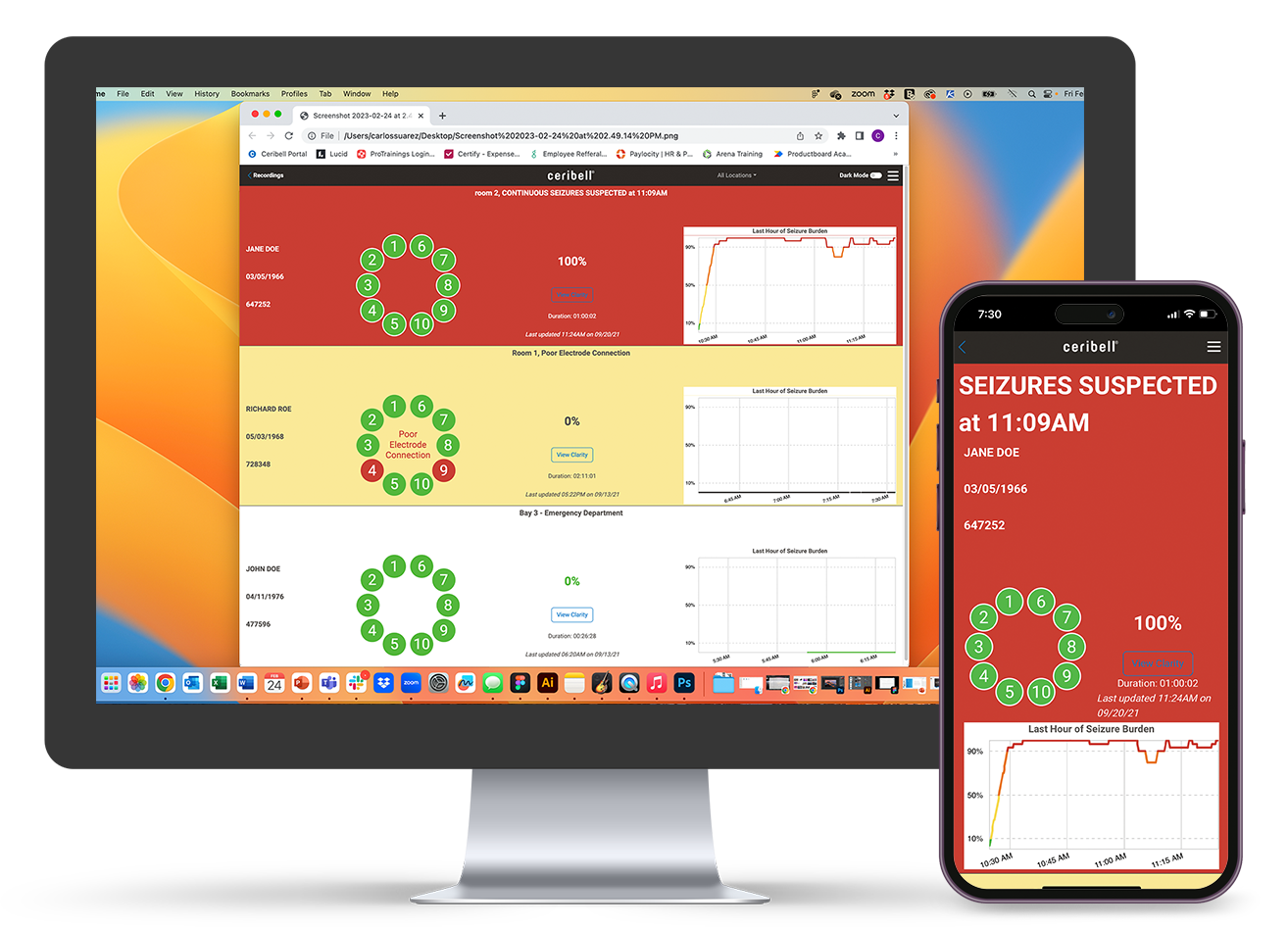

Insights Bar
Live Recordings Dashboard
Bedside ESE Diagnosis

Clarity aligns with both NCS and ACNS guidelines, enabling your hospital to comply with the latest recommendations and standards of care.
2012 NCS Guidelines
To minimize the amount of time a patient is in status epilepticus, the Neurocritical Care Society defines status epilepticus as 5 minutes or more of continuous clinical and/or electrographic seizure activity. The primary bedside alarm for Clarity alerts in accordance with these guidelines.
2021 ACNS Guidelines
The American Clinical Neurophysiology Society redefined Electrographic Status Epilepticus in 2021 as 10 continuous minutes of seizure OR 12 minutes of seizure activity in the last 60 minutes. Ceribell is the first and only company to diagnose Electrographic Status Epilepticus according to ACNS guidelines.

ESE is a life-threatening condition that is associated with
significant increases in morbidity and mortality. If left uncontrolled,
negative outcomes for ESE (including permanent disability or death) are
significantly increased.
Outcomes for patients with ESE are strongly tied to how quickly the condition
is recognized and controlled. Furthermore, efficacy of first line treatments
decreases as seizure duration increases further emphasizing the critical need
for rapid detection of ESE.¹
The ability to diagnose ESE is essential to detecting status epilepticus.
Neurocritical Care Society guidelines recommend that SE should be
controlled within 1 hour of onset.²
Despite these challenges, early diagnosis and management of SE have been shown
to dramatically improve patient outcomes.³
SE affects up
to approximately 200,000 or more Americans each year.4-6
Learn more at neurocriticalcare.org
References
MK-00440 rB
